Cracking
Also: coke, burn
If the hot-melt adhesive is heated too much, or operated over a longer period of time at excessively high temperatures, the overheating causes the macromolecules of the adhesive to break.
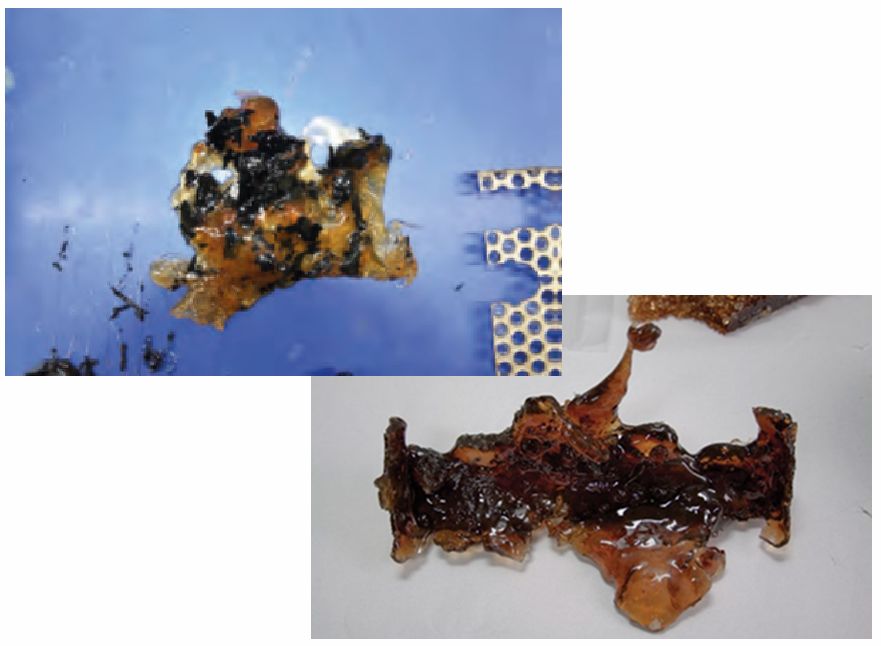
The change in the chemical composition can be seen in dark / black discolorations within the melt or in deposits on the tank walls. In some varieties, the formation of a gel-like skin layer on the melt can be observed.
Cracking is caused by:
- Too high temperature in the tank / no removal of hot-melt adhesive
- Too high temperature in the hose and / or in the application head
- External contamination / Introduction of foreign particles
These residues can spread throughout the entire application system and, in the worst case, impair the bond. These decomposition products have either no or only reduced adhesive properties. If these burnt adhesive residues get into the conveyor system, filters, hoses and nozzles will become clogged.
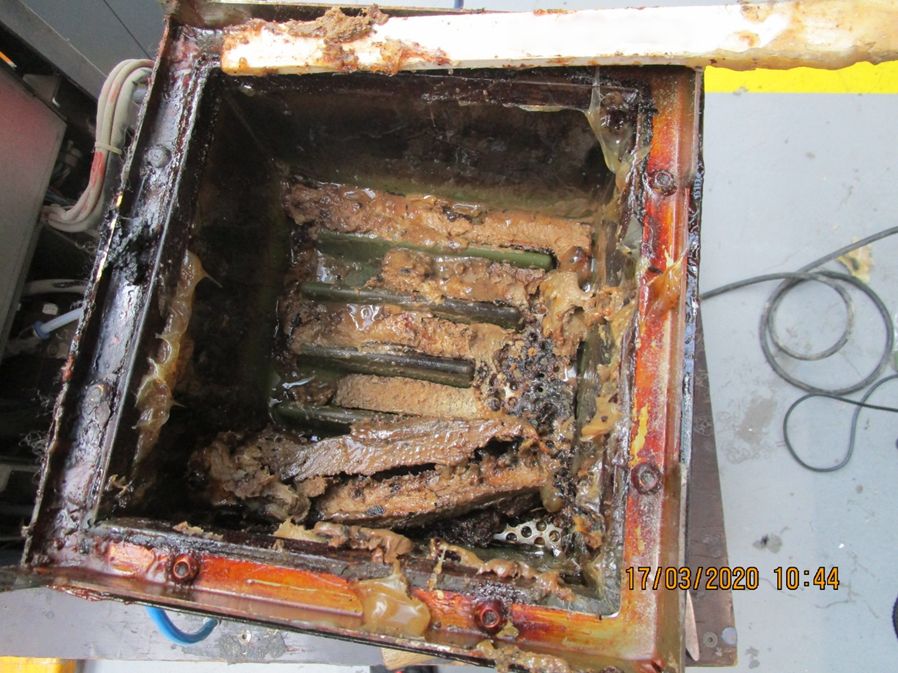

To prevent this, the application system (tank, nozzles, hoses, application heads, etc.) should be equipped with filters and sieves. These should be replaced regularly in the course of system maintenance.
Production downtimes caused by a machine failure can be avoided through regular cleaning phases. Regular cleaning of the accessible components is recommended as part of the daily working routine.
Stability in the melt is increased by lowering the temperature during breaks / downtimes.
Oxidation-stable hot-melt adhesives, such as BÜHNEN avenia, have a number of improved properties compared to conventional hot-melt adhesives. The thermal stability and the associated high process reliability in use is a point to be emphasised.
