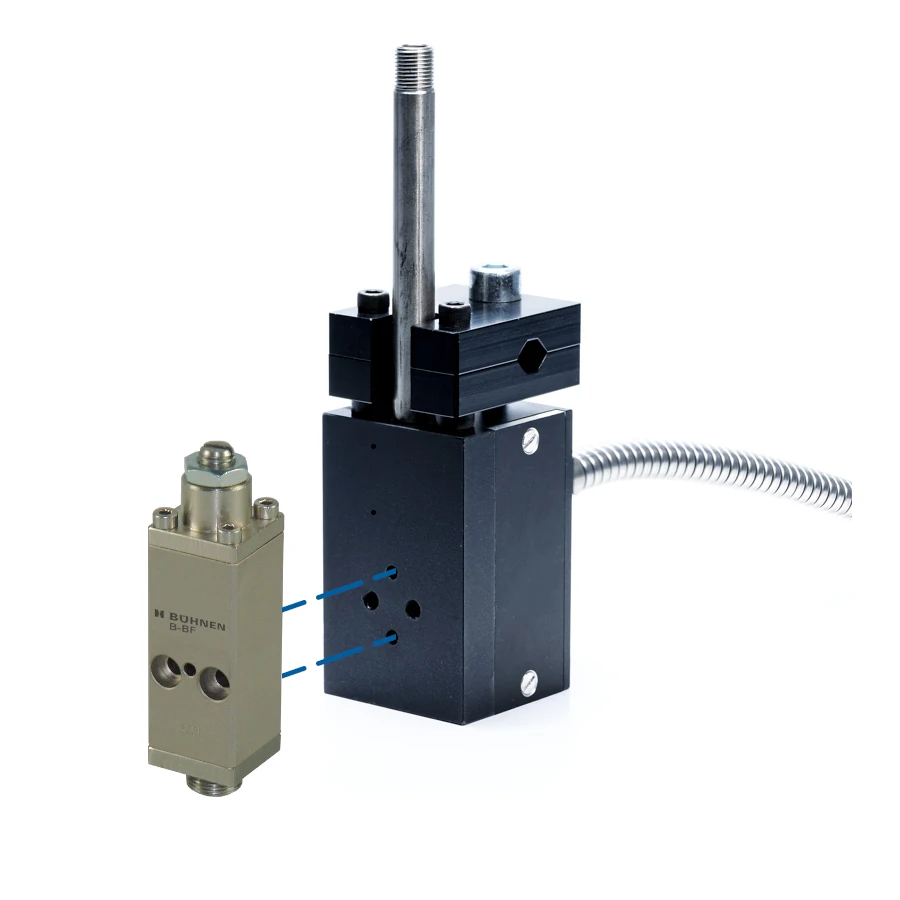
How an adhesive module functions
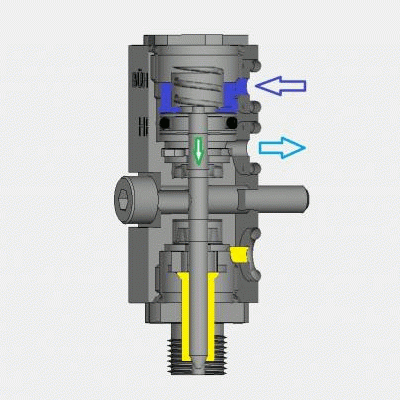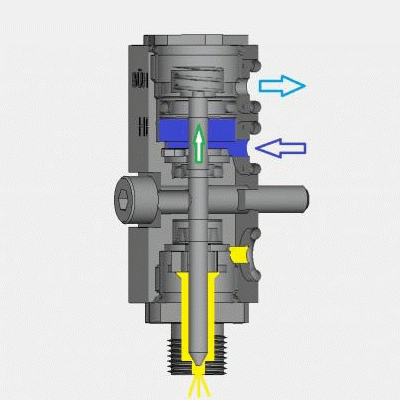
Air-opening / Air-closing
A module in a hot-melt application head performs a crucial function in controlling the flow of adhesive. These modules are screwed in front of the body of the application head and are responsible for precisely controlling the flow of adhesive.
Inside the module is a piston that is connected to a nozzle needle. This needle can open or close access to the nozzle of the application head.
There are two main types of modules: air-opening / spring-closing and air-opening / air-closing.
In the case of the first type, air-opening / spring-closing, the module is opened by compressed air. When compressed air is supplied, the piston moves to open the needle and allow adhesive to flow.
After the compressed air is switched off, a built-in compression spring ensures that the nozzle needle is closed automatically. This mechanism ensures a reliable seal and prevents adhesive from leaking after the application process is completed.
In contrast, with air-opening / air-closing, the compressed air must be used for both opening and closing of the module. When compressed air is supplied, the piston moves to open the nozzle needle and allow adhesive to flow.
To close the module, the compressed air is switched to move the piston in the opposite direction and close the nozzle needle.
In both cases, these modules allow precise control over hot melt adhesive flow, which is crucial to applying the correct amount of hot-melt adhesive to the substrate. The choice between the two types depends on the specific requirements of the application, but both variants ensure reliable control of adhesive flow for high-quality and consistent bonding.

